Introduction
Freight transportation is a central element in nearly every supply chain and is almost exclusively powered by fossil fuels. The logistics industry’s significant contribution to carbon dioxide and greenhouse gas emissions makes it a crucial contributor to climate change. So, numerous Carbon-Neutral policies including carbon offset in logistics are promoted to reduce their environmental impact. But carbon offsetting in logistics needs a lot of effort to make the results fruitful.
The Surprising Carbon Footprint of Logistics

A Global Concern
In 2015, global logistics transport by trains, ships, planes, and trucks emitted 2.9 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide (CO2). If business continues as usual, experts predict that this figure will more than double by 2050.
Despite ships being responsible for almost 75% of global cargo movement, road transport still accounts for 62% of all logistics emissions.
The logistics sector is responsible for around 8% (11% if warehouses and ports are included) of global emissions, making it one of the most carbon-intensive industries. Unless there is a widespread and coordinated effort, the transportation sector is on track to surpass the energy sector as the most carbon-intensive sector by 2040.
An Indian Headache
The logistics industry in India has a valuation of INR 11 lakh crore and is anticipated to experience a 7% growth rate.
Annually, India transports approximately 4.6 billion metric tonnes of cargo, resulting in a demand for transportation spanning 2.2 trillion tonne-kilometers and producing 2.3 gigatonnes of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions.
According to experts, this demand is expected to increase in the coming years, resulting in a significant rise in road freight transportation to reach 9.6 trillion tonne-kilometers by the year 2050.
Exploring Carbon Offset in logistics and associated strategies
Carbon offsetting is a practice aimed at counterbalancing the greenhouse gas emissions produced by specific activities or industries by investing in projects that reduce or capture an equivalent amount of emissions elsewhere.
Renewable Energy Initiatives
Logistics firms investing in wind, solar, or hydropower projects can help them to reduce their carbon footprint by sourcing clean energy.
Reforestation and Afforestation
Planting trees or restoring forests can capture significant amounts of CO2 from the atmosphere, making it an attractive option for Carbon offset programs of logistics firms.
Methane Capture and Reduction
Methane is a potent greenhouse gas which is emitted majorly from landfills, livestocks, and paddy cultivations. Capturing and utilizing methane or reducing emissions from these sources are valuable carbon offset in logistics.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
CCS projects capture CO2 emissions at the source and store them underground, preventing their release into the atmosphere.
Fun Fact: Carbon insetting is a practice of implementing Carbon reduction projects within the sector of impact. For example, in the logistics sector, utilising sustainable fuels, minimizing packaging, expanding e-fleets, indulge in engine retrofits and equipment decommissioning initiatives, building carbon-neutral warehouses, etc. will come under the Carbon Insetting measures.
FleetRobo has plenty of carbon insetting solutions. For example, combining FleetRobo’s Fuel Monitoring Solution and FleetRobo’s Video Telematics can facilitate efficient fuel usage and promote eco-friendly drives for your fleet. Similarly, with FleetRobo’s Logistics Process Automation you can automate the majority of your logistics operations and reduce energy-consuming tasks which will lead to Carbon emissions.
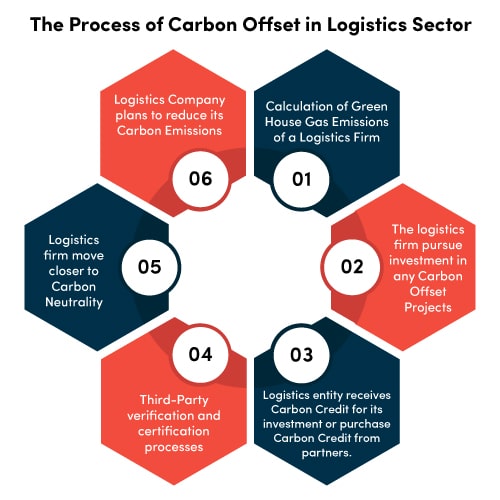
Fun Fact: Although carbon offsets and carbon credits are different, the terms often are used interchangeably. When a carbon offsetting project monetizes its efforts in the voluntary carbon market, it’s commonly referred as generating a voluntary carbon credit.
Move towards Carbon Offsetting in Logistics: Carbon Pricing, ULIP, and Maritime Sustainability
India’s Energy Conservation (Amendment) Act 2022
The legislation acknowledges the significance of carbon pricing and strives to establish a carbon market or an Emissions Trading System (ETS). This is applicable to the logistics sector as well.
Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP)
It is a government initiative which is part of the ‘National Logistics Policy (NLP)’. ULIP seeks to curtail emissions originating from logistics operations. It achieves this objective by establishing a platform that facilitates the exchange of information among logistics firms and encourages collaborative efforts toward emission reduction.
IMO’s Energy Efficiency requirement for vessels
India has committed to implement IMO’s energy efficiency requirements for existing ships and carbon intensity requirements for all vessels. Indian Ports are expected to adhere to all the targets which are in line with nine UN Sustainable Development goals.
The Advantages of Carbon Offsetting in Logistics: A Sustainable Path Forward
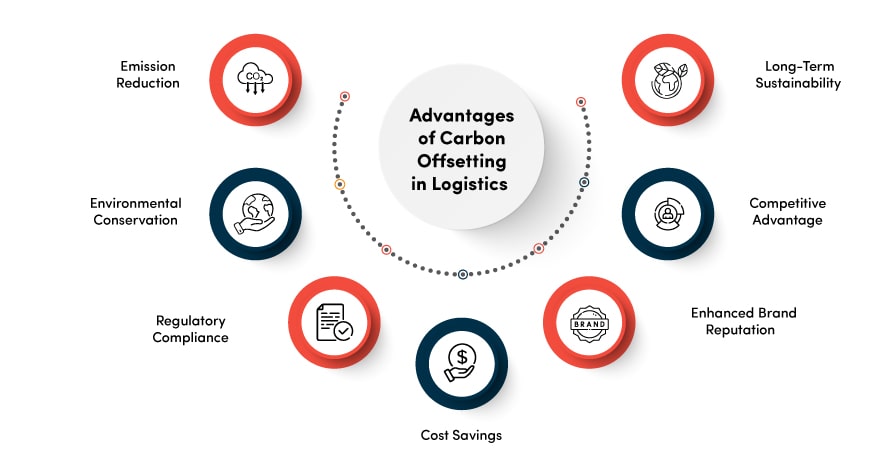
Emission Reduction
Carbon offset projects directly reduce or capture greenhouse gas emissions elsewhere. Hence, they effectively neutralizing the emissions generated by logistics activities. This contributes to the overall reduction of carbon dioxide and other harmful gases in the atmosphere.
Environmental Conservation
The primary advantage of carbon offsetting in logistics is decreased carbon emissions in logistics. Thereby, contributing to the fight against climate change and the lessening of the environmental footprint associated with logistics operations.
Regulatory Compliance
Carbon offset projects empower logistics companies to meet and surpass the stringent environmental regulations and emissions reduction targets set by governments and international agreements. This helps them demonstrate their commitment to environmental responsibility and sustainability.
Cost Savings
Investments in carbon offset programs often lead to cost savings in the long run. For example, adopting renewable energy sources or enhancing energy efficiency measures can result in decreased fuel consumption, reduced energy expenses for facilities, and lowered maintenance costs for environmentally friendly vehicles and equipment.
Enhanced Brand Reputation
Organizations that achieve significant carbon offsetting in logistics can showcase their dedication to environmental stewardship. This commitment can bolster the logistics brand image and draw environmentally conscious customers and collaborators.
Competitive Advantage
Embracing carbon offsetting in logistics can position logistics companies as pioneers in sustainable logistics, offering a competitive advantage in the market. It can open doors to new business opportunities and partnerships with like-minded organizations.
Long-Term Sustainability
Carbon offset programs contribute to the long-term sustainability of both the environment and the logistics industry itself. For instance, logistics entities can mitigate the volatility of energy prices and supply chain disruptions due to climate-related events. Together, it can ensure Supply Chain Resilience.
Challenges and Pitfalls in Carbon Offset in Logistics
Absence of Standardization and Oversight
The absence of uniform standards and regulations regarding carbon offset targets can result in disparities in the quality and trustworthiness of offset initiatives done by logistics firms.
The lack of carbon accounting
Many logistics companies don’t track their carbon emissions through proper digitalized methods. This led to serious under estimation of carbon emissions in the logistics sector. This potentially hinder their carbon offsetting activities.
A Potential Way to Deviate from Other Green Initiatives
Carbon offset programs can potentially lead to a moral hazard scenario. Ideally, a logistics firm should aim to achieve a blend of both green logistics and carbon offsetting practices. However continuing carbon offset in logistics might make the logistics firm believe that by buying offsets, they can effectively be compensated for their emissions. This might neglect them to control their emissions.
The issue of Greenwashing
Carbon Offsetting Projects are often considered by Logistics companies as a marketing tool to create a positive image without meaningful emission reductions. This not only undermines the credibility of carbon offsetting in logistics but also hinders the genuine projects and projections of carbon offsetting in logistics.
FYI: Greenwashing refers to the deceptive practice of portraying an organization’s products as environmentally friendly through false information or misleading claims. It entails making unsupported claims regarding the environmental friendliness of a company’s products to mislead customers.
Driving Carbon Offsets in Logistics: Collaborative Strategies for a Greener Future
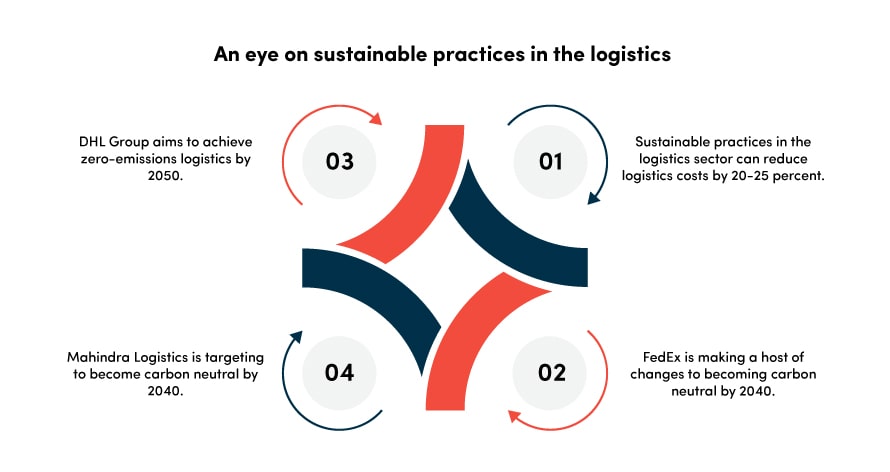
To fulfill India’s commitment to the Net Zero emissions by 2070, the logistics sector’s contribution to decarbonization is essential. Here are some approaches that can be embraced to accomplish this objective:
Eco-friendly Policies and Incentives
Different regulatory and industry organizations should implement favorable policies and incentives to promote environmentally sustainable practices. Such as promoting renewable energy adoption, offering tax benefits for eco-friendly initiatives in logistics, etc.
Cookstove approach for Carbon Offset in Logistics
Cookstoves fuelled by wood, coal or fossil fuels emit CO2, as well as black carbon. Carbon offset funds are regularly used to replace high-emitting cookstoves with cleaner cookstoves. In 2017, over two million tonnes of eliminated cookstove CO2 emissions were sold on the voluntary carbon offset market.
Similarly, trucks make up only one-quarter of the global diesel road fleet but contributing 78% of its black carbon emissions. Like the clean cookstove project, Fleet renewal In logistics has to be done to replace the older trucks within the fleet pool with newer emission control compliance trucks. These carbon offset trucks will not only reduce emission but also reduce the maintenance cost associated with the older ones.
Conclusion
The logistics sector will remain a crucial factor in shaping a sustainable future. Firms can actively participate in building a more environmentally friendly and robust supply chains by spearheading inventive carbon offsetting projects.
The logistics firms should move beyond the carbon offset projects and explore ways towards achieving carbon neutrality by taking steps towards green warehousing practices, adopting eco-friendly transportation practices, and optimizing the use of road transport. For instance, with FleetRobo’s Logistics Process Automation, you can improve TAT, and automate security checks and weighbridge. Similarly, with FleetRobo’s Fuel Monitoring Solution, you can optimize routes for efficient fuel usage. Likewise, with FleetRobo’s Video Telematics, you can promote Eco-Driving by monitoring and averting overspeeding traffic violations & harsh braking.
In conclusion, the firm can reduce overall ecological footprint in Logistics and enable the logistics sector to be better prepared for future challenges.
To get more details please visit the FleetRobo’s website.

